Protecting Cloud Data Throughout Its Lifecycle
Organizations have flocked from on-premises to the cloud over the past year, and protecting data during the transition has proven to be a monumental task. But now companies must focus on what happens after the migration.
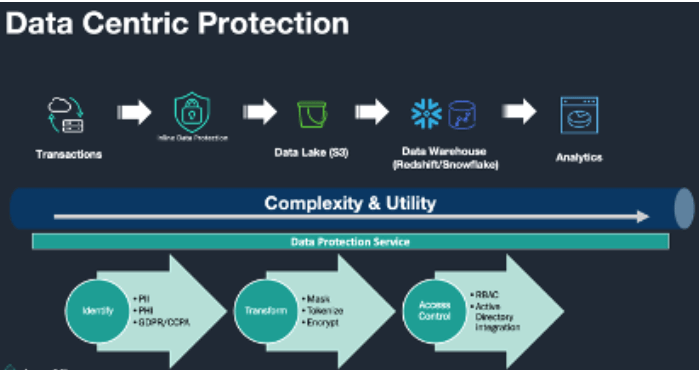
The new reality is that these organizations and their cloud providers work under a shared responsibility model, in which the provider protects the cloud infrastructure and the customer protects the data inside the cloud. This means that they need an advanced, data-centric security approach that protects their sensitive data throughout various phases of its lifecycle: identification and discovery, transformation, protection and sharing.
● Identification and Discovery Phase. Upon data creation—and before entering the data analytics pipeline—it is critical to determine relative sensitivity of breach risk and apply protection methods that are appropriate. Companies must also determine what is considered personally identifiable information (PII) based on applicable compliance standards (e.g., GDPR or CCPA) and eventual use. Applying this information using detailed metadata also helps clear up any confusion about what a piece of data is and how sensitive it is.
● Transformation Phase. Once data has been deemed sensitive, the transformation phase begins. If the data is not to be utilized downstream, it can be masked. If the data is required to look similar to the original data, it can be tokenized, a process by which unrelated, scrambled characters of the same format disguise its value. For example, a tokenized Social Security number would consist of nine random numbers, so it looks like an actual SSN. This method disguises a piece of data with dummy characters and hides its real value.
If the data is to be utilized in its original form but without exposing it in the clear, homomorphic techniques, such as secure multi-party compute (SMPC), must be deployed. This is now known as Privacy Preserving Computing (PEC), a Gartner Top 10 Strategic Technology Trend for 2021. It starts with encrypting the sensitive data using the AES-256 algorithm, which has proven to be cryptographically secure. This process converts data into unreadable ciphertext. Bring Your Own Key (BYOK) is emerging as a standard compliance requirement for regulated industries, such as financial services and healthcare. BYOK helps organizations protect their cloud data by enabling encryption or tokenization of sensitive data records using keys that only they can access, effectively giving them the “right to be forgotten.”
● Access Control and Sharing Phase. Transformed data is protected when it is at rest. But to ensure that data breaches are prevented, access to it must be carefully controlled. Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) is one such capability that allows for granular policy-based control based on an employee’s persona. For example, a test and development engineer may only need access to tokenized data, while a data scientist may need the actual data to run algorithms. With RBAC, it is possible to create such adaptations or views of protected data. As more data is collected and the benefits of data analytics are realized, enterprises understand that their analyzed data alone is not enough to garner the insight necessary for market differentiation.
Sharing data with other organizations and lateral partners provides deeper analysis and context to guide critical business decisions. To share data safely, organizations can use PEC techniques to securely share data across multiple disparate organizations without letting other participating organizations see anyone else’s sensitive data. The benefit of this approach is that private data remains private, but collectively, organizations can process the data for analytics and business intelligence. This capability can address problems like anonymized threat detection or healthcare outcome analysis, in which multiple parties generate sensitive data that needs to be processed by a third-party data processor. One would only need to allocate a unique key to each data generator, encrypt that data with it and share the key with the data processor to analyze without ever revealing the actual data in the clear.
Enterprise dependence on the cloud has accelerated to unprecedented levels, and the days of an on-premises-first environment are in the rearview mirror. Cloud computing requires a new way of looking at security to ensure that data, which holds the potential of enormous ROI, is protected responsibly regardless of how, when or where it is being used.
Learn more about how Baffle helps enterprises with its data protection service for protecting the data analytics pipeline, including secure data sharing.
Join our newsletter
Schedule a Demo with the Baffle team
Meet with Baffle team to ask questions and find out how Baffle can protect your sensitive data.
Easy
No application code modification required
Fast
Deploy in hours not weeks
Comprehensive
One solution for masking, tokenization, and encryption
Secure
AES cryptographic protection
Flexible
No impact to user experience