Asking different people within software organizations or even different people within the security space to define “data masking” often means you will get different – and sometimes complex – answers. There are so many terms, pseudonyms, and technologies related to data masking that we wanted to get back to the basics. In this article, I’ll discuss the fundamental concepts of data masking, explain various masking techniques, delve into the difference between static data masking and dynamic data masking, and talk about Baffle’s Data Masking services.
 What is Data Masking
What is Data Masking
In data security, data masking is generally used as the catch-all term for the process of altering data to protect sensitive information. It can also be known as data obfuscation, data de-identification, data anonymization, and data sanitization. Additionally the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) introduced the term “pseudoanonymization” that covers a range of processes to protect sensitive data.
The goal of data masking is to allow sensitive data to be used while ensuring it is kept secure. To meet this goal, sensitive data must be masked using a method that ensures there is no way to reverse engineer the process and gain access to the original data.
Data Masking Techniques
There are many different ways to mask sensitive data, and there are pros and cons to each type of masking. To make the decision on how to mask your data, it’s important to understand the various techniques, how you want to use the data after it’s masked, and who will have access to the data.
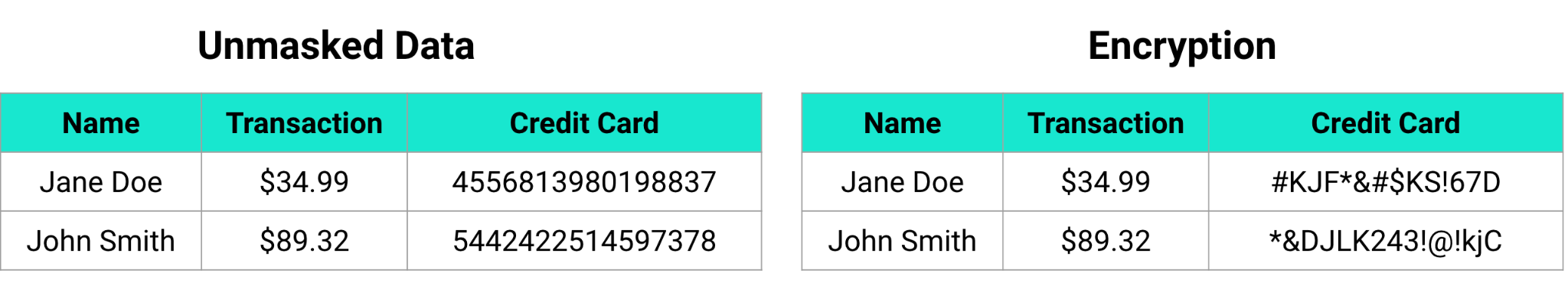
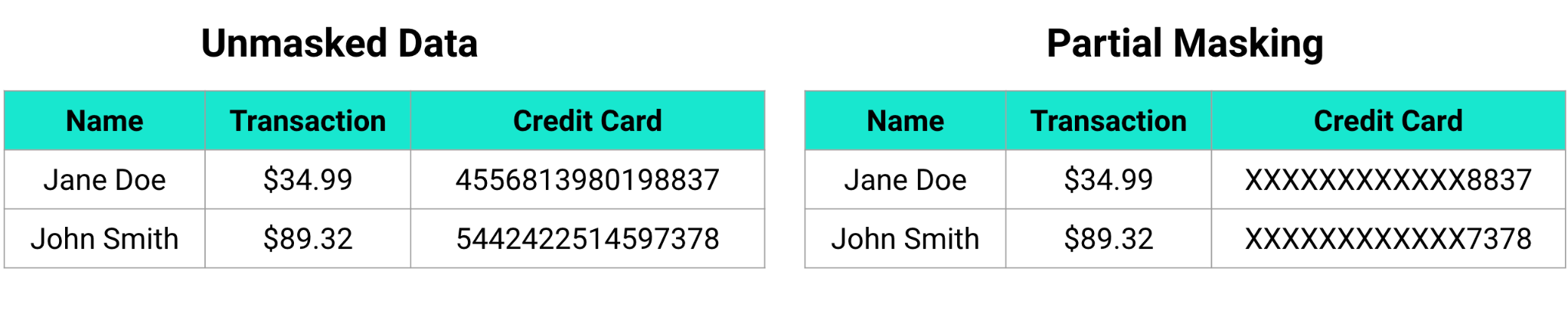
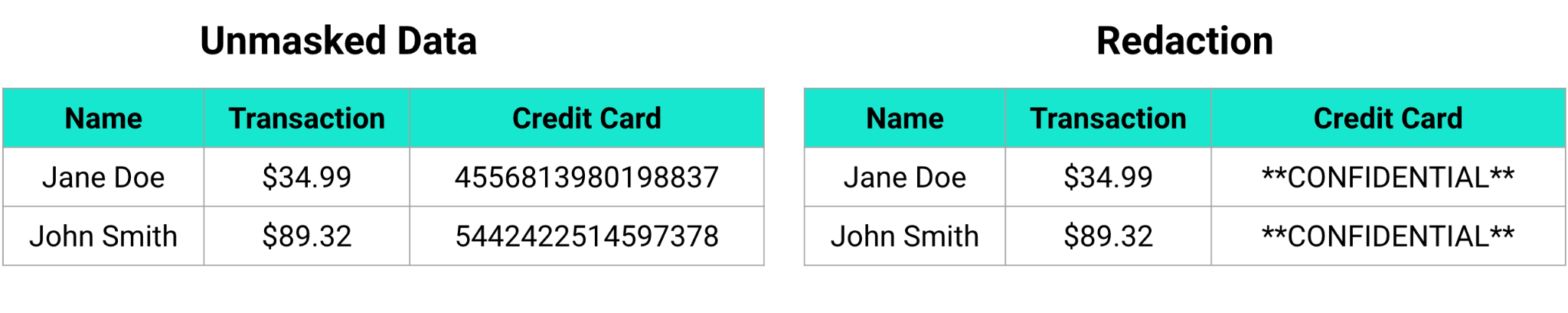
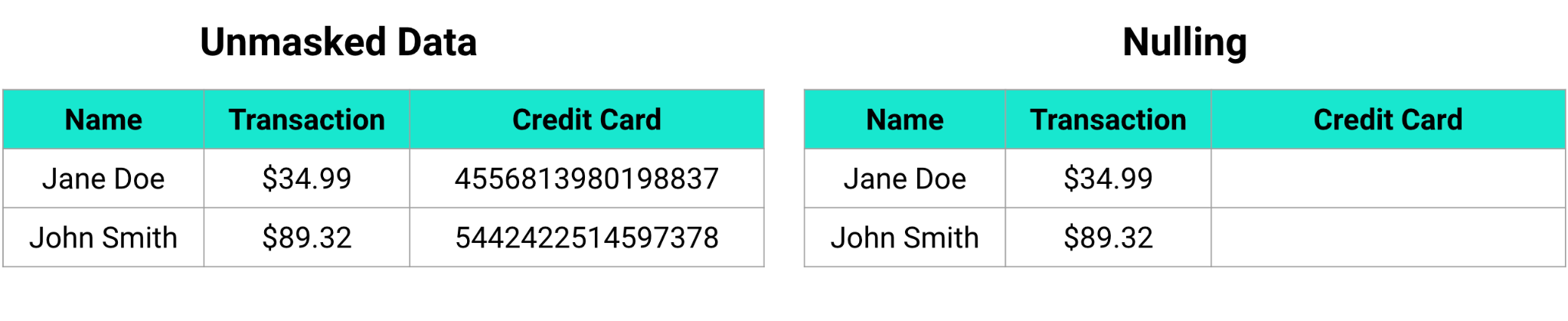
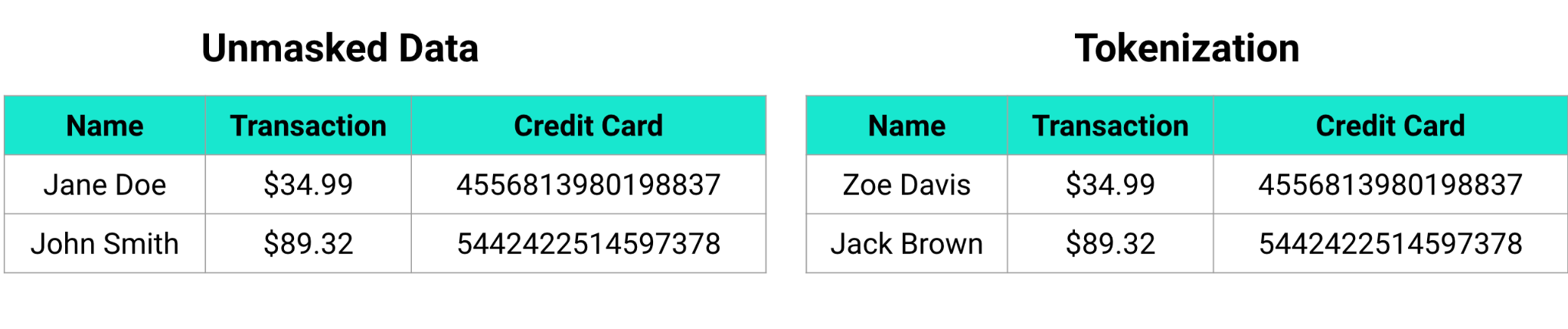
Static versus Dynamic Masking
Now that we’ve discussed masking techniques, it’s important to discuss the method in which data is masked. All of the above masking can either be done via static data masking or dynamic data masking.
Static data masking is when you directly alter the data with an anonymized value. This is typically done on a copy of your data (a replica) so as not to lose the original values. That replica can then be used elsewhere safely. The biggest advantage to static data masking is that the masked data can never expose the sensitive value. The biggest disadvantage is that you have to maintain a masked version and an unmasked version of your data. With ever increasing amounts of data within organizations, this can be incredibly costly.
Dynamic data masking is when masking occurs only when the data is viewed. Dynamic data masking is powerful because it allows role-based access controls to be implemented and does not destroy the original data value. This means with the appropriately configured security policies, a supervisor can see the data in cleartext, but all other users only see masked data. Dynamic masking allows greater control over access to the data and expands the use cases your data can serve.
Data Masking with Baffle
As you can see, there are many different ways you can mask sensitive data. Baffle’s Data Protection Services gives you the ability to choose any of these data masking methods, or a combination of these methods. While we believe encrypted, dynamic data masking to be one of the best and most secure options out there, we also understand that may not be desired for every data use in every situation. Our flexible platform provides you robust options to mask your sensitive data the way you want to mask it, and to enable both field-level and record-level data masking. We do all of this with no application code changes, helping you avoid lengthy projects to protect your data.
Learn More
To see a demo of data masking and discuss your data protection concerns, please schedule a meeting with Baffle.
Join our newsletter
Schedule a Demo with the Baffle team
Meet with Baffle team to ask questions and find out how Baffle can protect your sensitive data.
Easy
No application code modification required
Fast
Deploy in hours not weeks
Comprehensive
One solution for masking, tokenization, and encryption
Secure
AES cryptographic protection
Flexible
No impact to user experience



